Oral sex refers to when a person puts their mouth, tongue, or lips on the genitals or anus of another person.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that people can pass on through oral sex can infect multiple parts of the body, including the:
- mouth
- throat
- genitals
- rectum
In this article, we take a look at STDs that people can spread through oral sex and their signs and symptoms.
We also cover how people can transmit these STDs, along with their treatment options.
Pictures

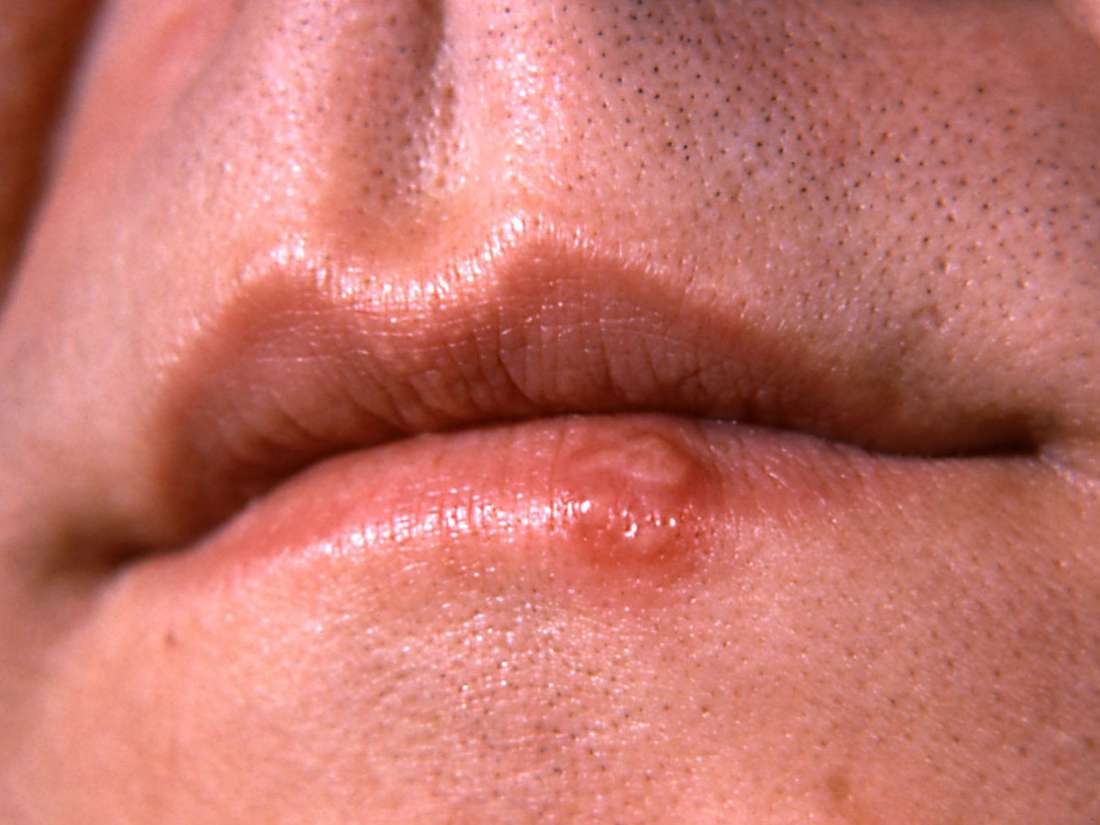
Gonorrhea
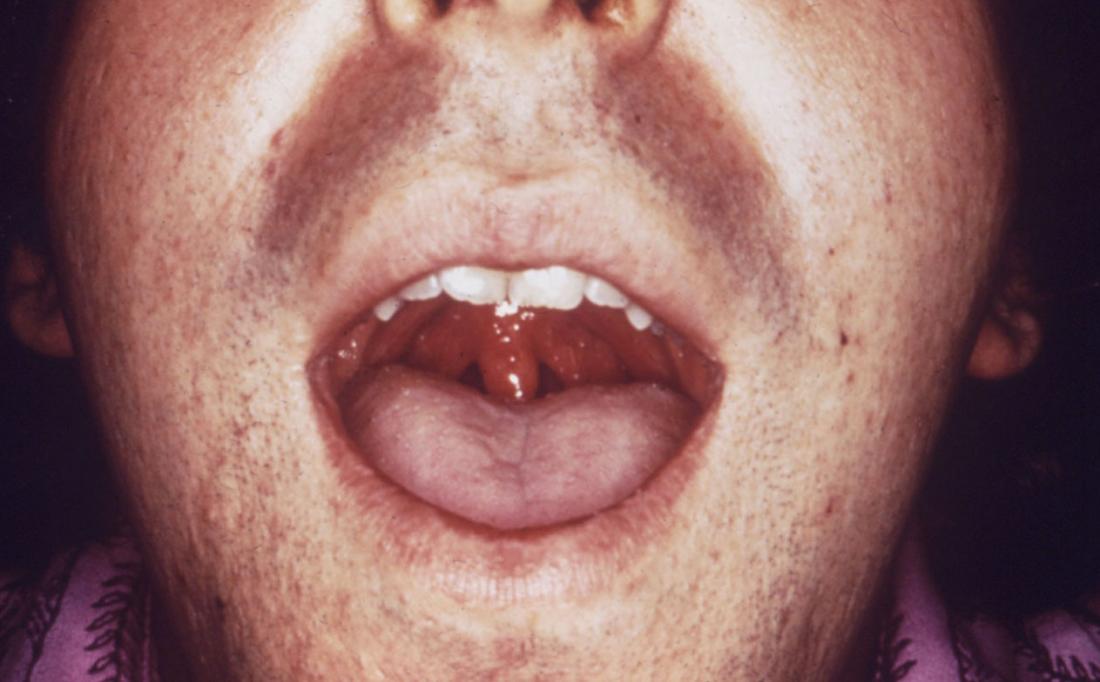
Image credit: CDC/ Dr. N. J. Flumara, Dr. Gavin Hart,1976.
Gonorrhea
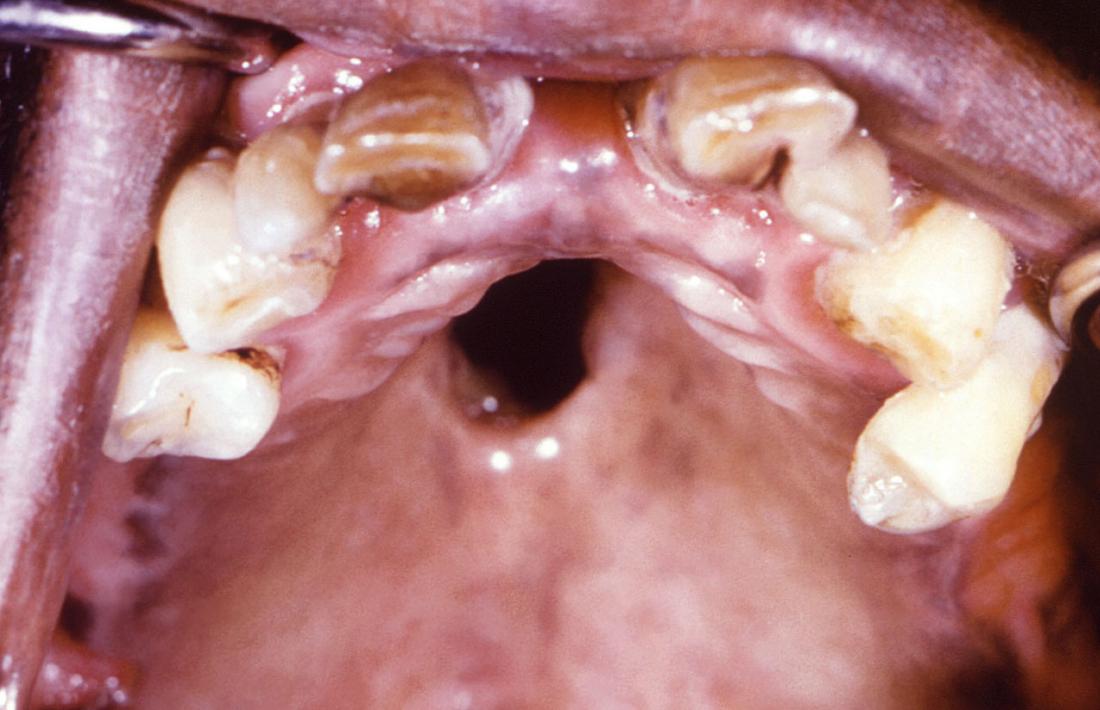
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
Syphilis
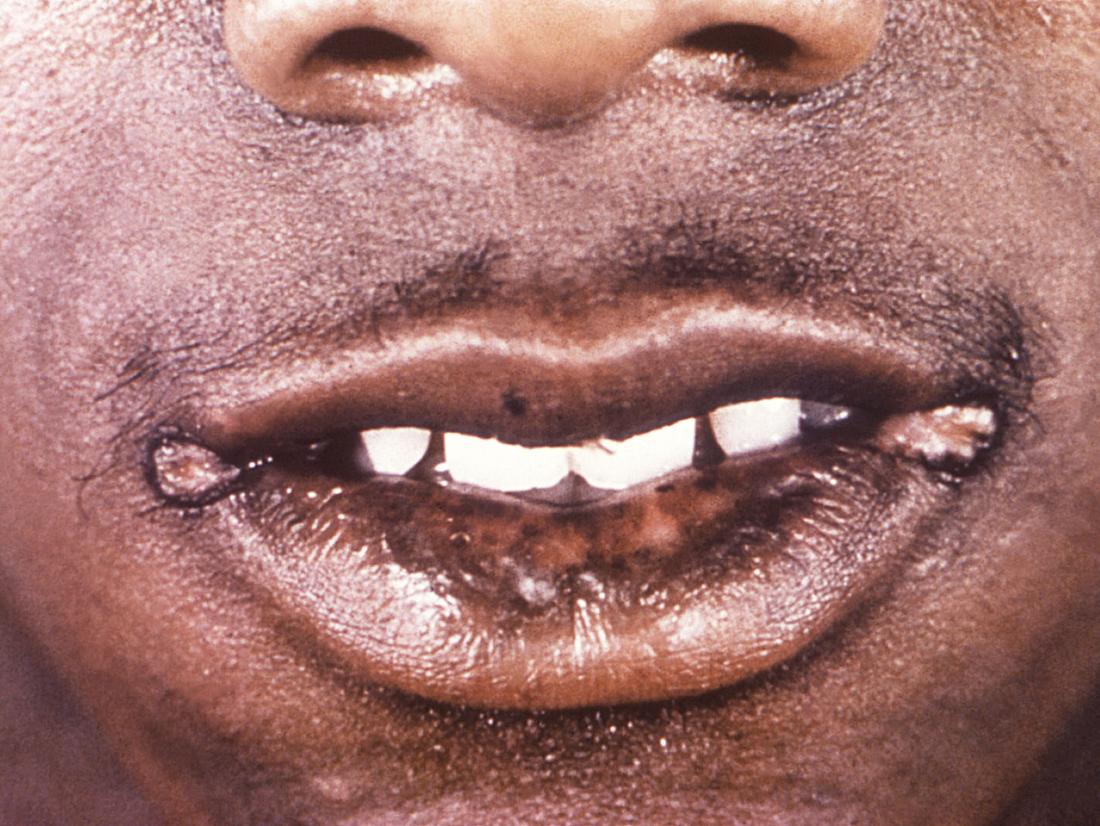
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
Syphilis
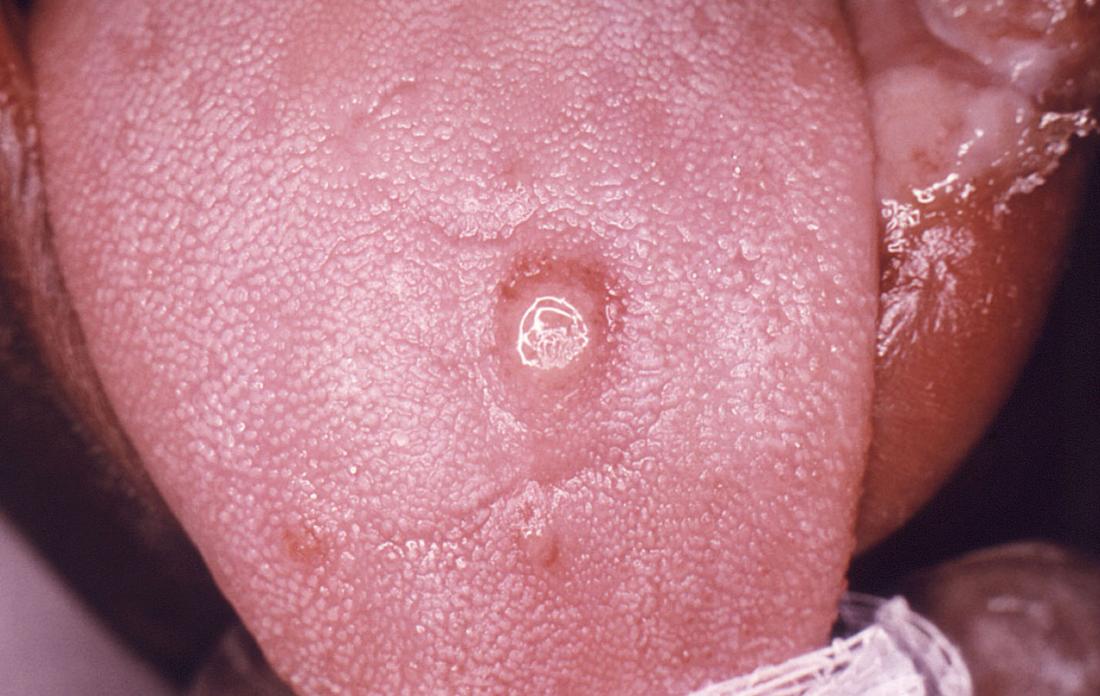
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
Syphilis
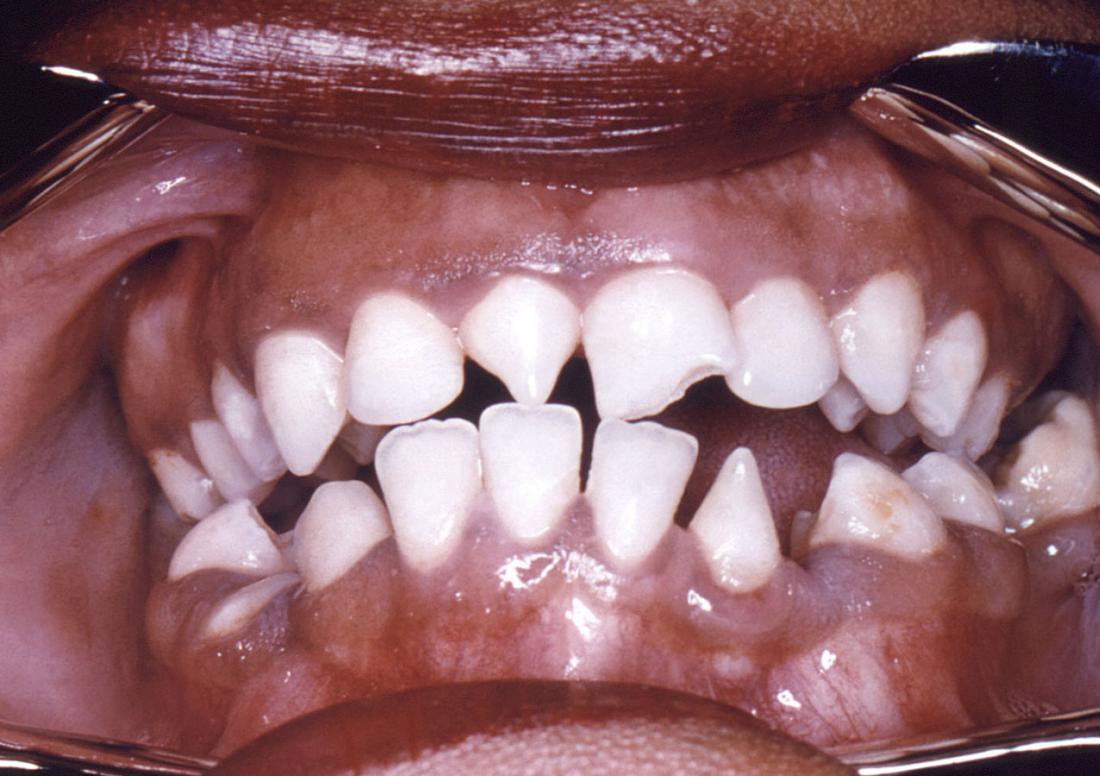
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
Syphilis
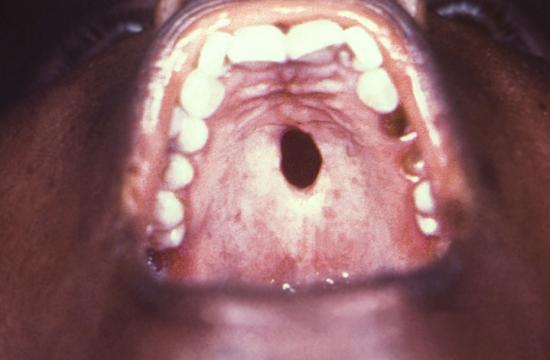
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
HPV
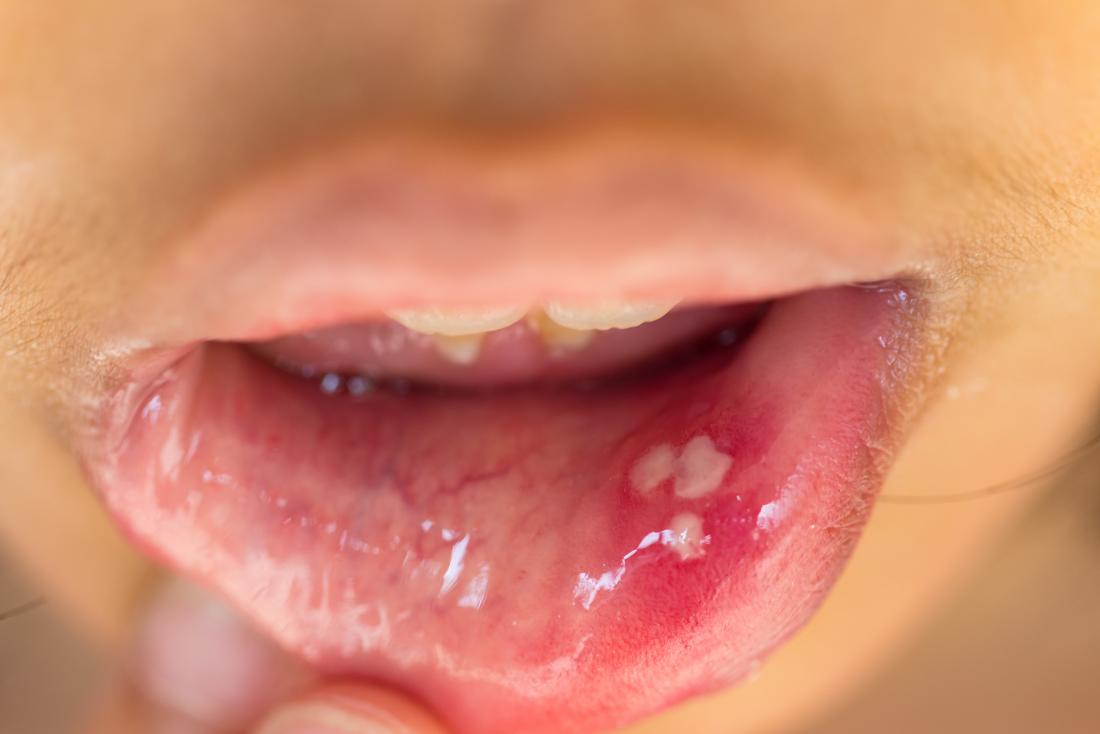
Herpes
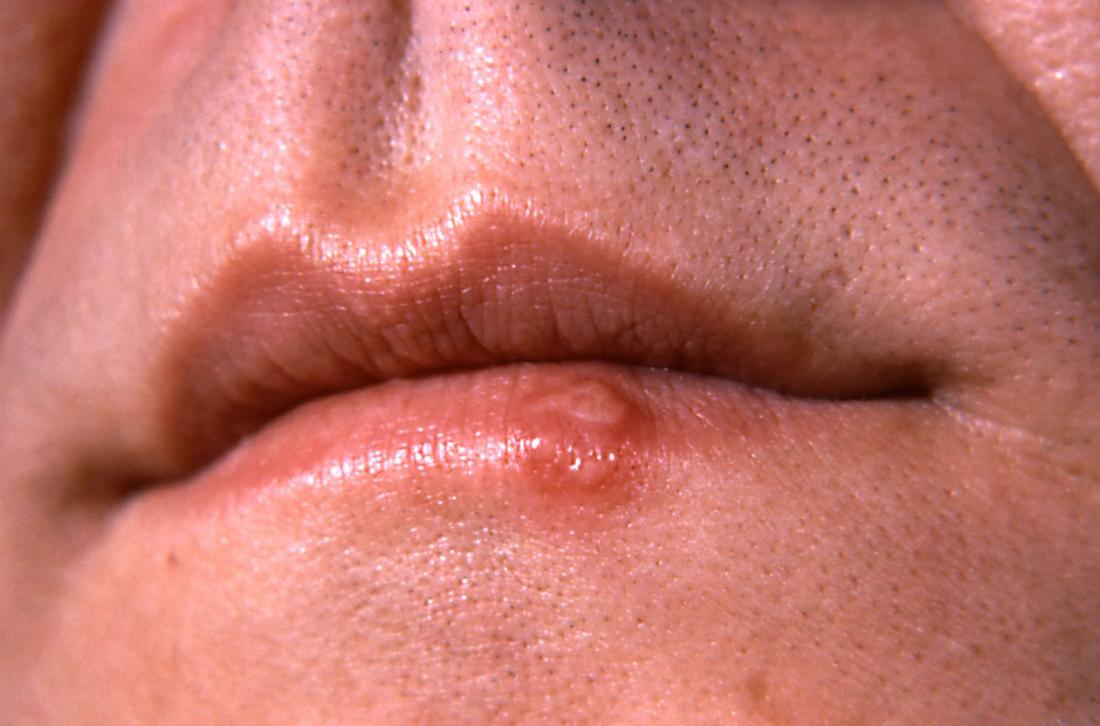
Image credit: CDC/ Dr. Hermann, 1964
Herpes
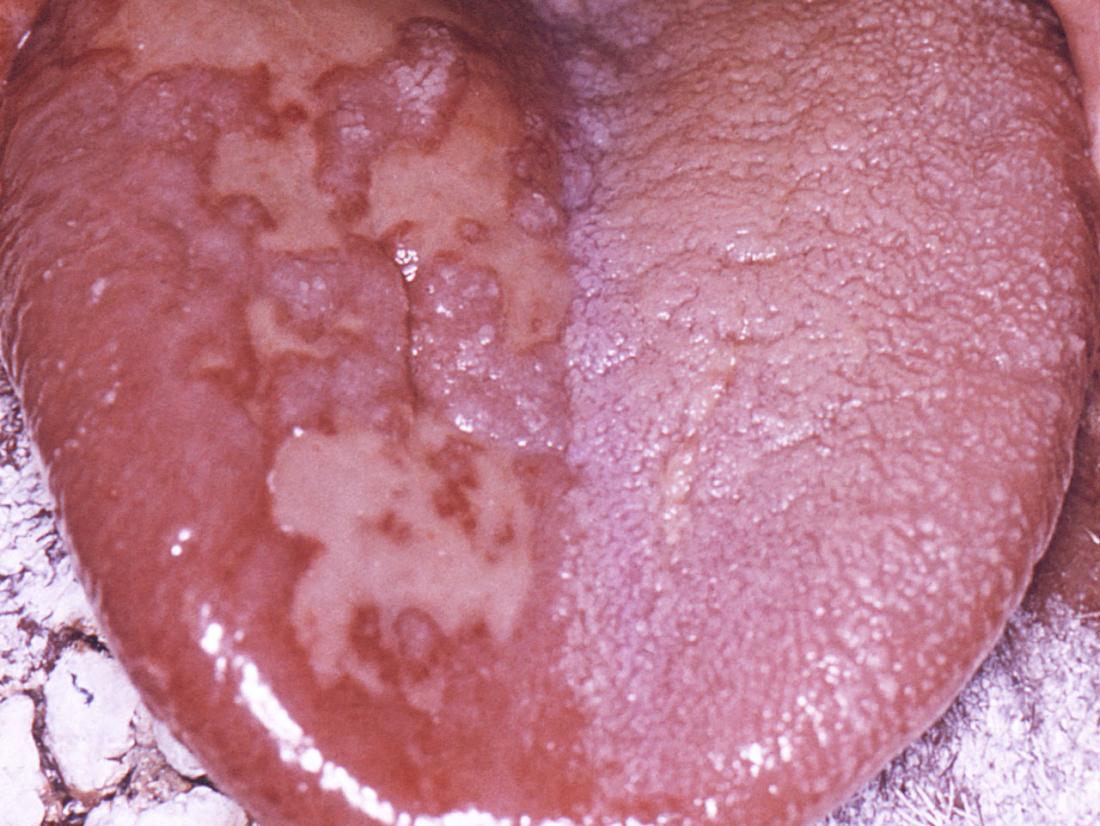
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
Herpes
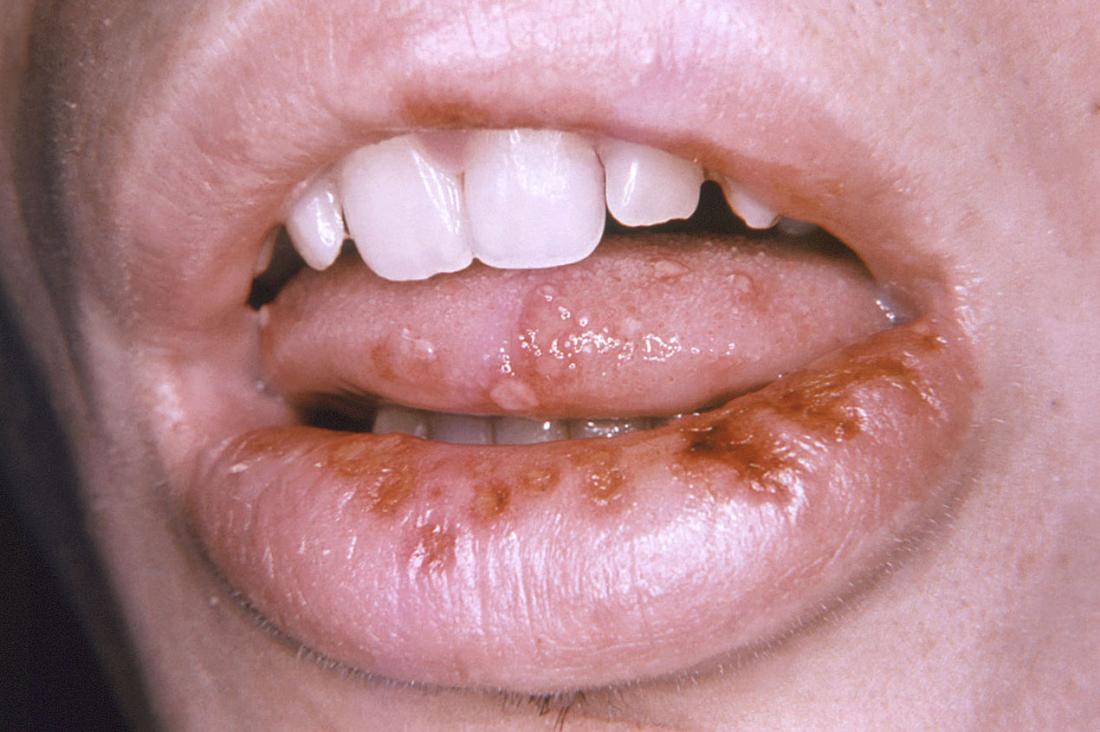
Image credit: CDC/ Robert E. Sumpter, 1967.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an STD that Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria cause.
Symptoms
Gonorrhea does not always cause symptoms. If people do notice symptoms, they may include:
- a burning sensation when urinating
- a sore throat
- unusual discharge from the vagina, penis, or rectum
- swelling or pain in the testicles
- pain in the rectum
Transmission
People can get gonorrhea as a result of having oral sex with someone who has a gonorrhea infection in the throat, vagina, penis, urinary tract, or rectum.
Diagnosis and treatment
A doctor can take a urine sample to test for gonorrhea. They may also take a swab from the:
- throat
- rectum
- urethra in males
- cervix in females
Gonorrhea is treatable with antibiotics, though some strains have now become resistant to antibiotics.
If people continue to experience symptoms after receiving treatment for gonorrhoea, they should see their doctor again.
Outlook
If a person does not seek treatment for gonorrhea, it can cause serious health complications, including:
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria can cause.
Symptoms
Chlamydia infections often have no symptoms.
However, if a person has a chlamydia infection in their throat, they may have a sore throat.
If they have an infection of the rectum, genitals, or urinary tract, symptoms may include the following:
- unusual discharge, such as blood, from the vagina, penis, or rectum
- a burning sensation when urinating
- pain in the rectum
- swelling or pain in the testicles
Transmission
People can get chlamydia as a result of having oral sex with someone who has a chlamydia infection. People with a chlamydia infection in the throat, vagina, penis, or rectum can pass on the infection.
Diagnosis and treatment
Doctors can diagnose chlamydia by taking a urine sample or a vaginal swab for females.
People can treat chlamydia by taking antibiotics. They should avoid having sex until they have completed the course of treatment.
Outlook
Chlamydia is treatable with antibiotics. It is important that people seek treatment for chlamydia, as it can spread to a sexual partner if they do not treat it.
It can also cause serious health problems, including:
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that Treponema pallidum cause.
Symptoms
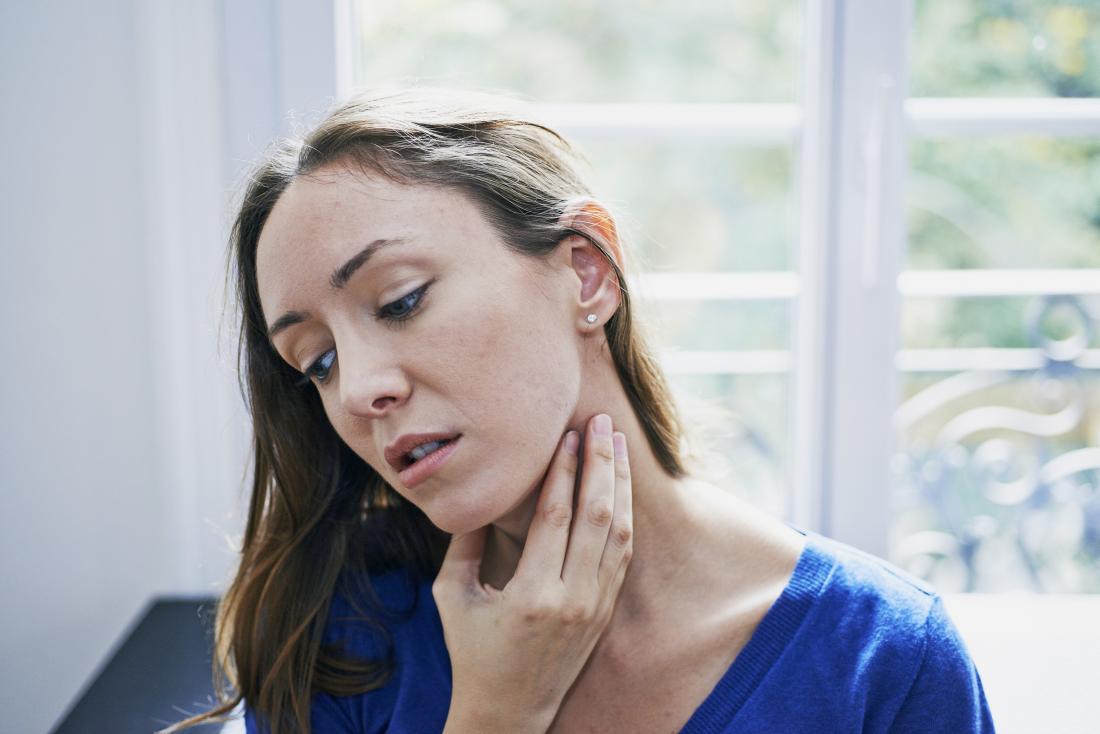
Syphilis can cause swollen lymph nodes and a sore throat.
People may not notice any symptoms from syphilis, and the first signs are usually mild. There are four stages of a syphilis infection, and each stage has different symptoms:
Primary
- firm, round sores at the site of infection, which may be painless
Sores can last for 3–6 weeks and are self-healing. When the sore heals, the infection is still present. For this reason, it is important that a person continues to receive treatment.
Secondary
Even if these symptoms pass without treatment, it is essential that people still get treatment to remove the infection and prevent it from progressing to further stages.
Latent
The latent stage of syphilis has no symptoms. Without treatment, people may have a syphilis infection for many years without noticing any symptoms.
Tertiary
People do not usually develop tertiary syphilis, but it can happen 10–30 years after first getting the infection if they do not seek testing and treatment at the time.
People may notice severe complications if they have tertiary syphilis, which may include:
- damage to internal organs
- changes in vision
Neurosyphilis occurs when syphilis spreads to the brain or nervous system. Symptoms of neurosyphilis can include:
- headaches
- difficulty moving parts of the body
- numbness
- dementia
Tertiary syphilis can be fatal if a person does not receive treatment.
Transmission
People can get syphilis by engaging in oral sex with a person who has syphilis, specifically by coming into direct contact with a syphilis sore or rash.
Diagnosis and treatment
A doctor will take a blood test to check whether a person has syphilis. If people have sores, a doctor may test fluid from the sore.
The earlier people receive treatment for syphilis, the easier it is to cure. Doctors can use a penicillin injection to treat type of this infection.
Outlook
Syphilis can cause severe complications and can even be fatal if a person does not receive treatment. If left untreated, syphilis can cause:
- stillbirth
- increased risk of HIV
- damage to organs
- blindness
If someone has a syphilis infection while pregnant, they can also pass the infection to their baby.
Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common STD in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Symptoms
People with HPV may have no symptoms. However, HPV can cause:
- warts on or around the genitals or anus
- warts in the throat
If people have warts in the throat, they may feel breathless or have difficulty speaking.
Transmission
People can get HPV through giving oral sex to anyone who has an HPV infection in the genital area, anus, or rectum.
People with an HPV infection in the throat can also pass on the infection by giving oral sex to a partner.
Diagnosis and treatment
There is no specific test that healthcare providers use to detect HPV, especially in the mouth or throat. Some people may find out that they have HPV if they get an abnormal test result from cervical cancer screening, or a Pap smear.
Others may find out that they have it if they develop genital warts or other complications.
People can treat warts from an HPV infection but not the virus itself. A person can remove warts by taking certain medicines or undergoing surgery. Sometimes, the warts disappear by themselves.
Outlook
HPV often goes away without treatment.
Even if people treat the warts, they can still spread the HPV infection to sexual partners.
Some types of HPV can cause cancer, including cervical cancer. Many females do not develop cervical cancer if they receive the correct treatment for HPV.
People can get an HPV vaccine to help protect against the diseases that HPV can cause.
Herpes
Herpes is an infection that the herpes simplex virus can cause.
Symptoms
Herpes often produces no symptoms, or very mild ones. The main symptoms following initial infection may include:
- painful or itchy sores around the genital area, rectum, or mouth
- headache
- fever
- aching body
- swollen glands
Transmission
People can get herpes as a result of having oral sex if a partner has a herpes infection in the mouth, genital area, rectum, or anus.
Diagnosis and treatment
A doctor may take a skin sample from a sore for testing, or they may perform a blood test to help diagnose herpes.
Although there is no cure for herpes, people can take antiviral medicine to reduce or prevent the symptoms.
Outlook
With or without treatment, people can spread herpes infections to sexual partners. Taking daily medicine can help reduce the chance of passing on the infection, however.
Having herpes can increase the risk of getting an HIV infection, and pregnant women can pass on herpes to their infant.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, or trich, is a common infection that a parasite causes.
Symptoms
Symptoms can include:
- unusual discharge from the vagina or penis
- redness or itching around the vagina
- a burning sensation when urinating
Transmission
If people give oral sex to a partner who has a trichomoniasis infection in the vagina or penis, they may get a trichomoniasis infection in the throat.
Diagnosis and treatment
Treatment for trichomoniasis may involve taking a course of antibiotics.
People will need to see their healthcare provider for laboratory tests to check for trichomoniasis, as a doctor cannot diagnose it just from the symptoms.
People can treat trichomoniasis by taking a single dosage of antibiotic medicine that can also destroy parasites.
To prevent getting another infection, people should make sure that their sexual partners also receive treatment.
Outlook
People can easily treat trichomoniasis by taking oral medication.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hepatitis A tend to develop after an average of 28 days from exposure to the virus. These symptoms can include:
Transmission
Hepatitis A transmission mainly occurs through oral-fecal contact. As a result, a person could contract hepatitis A by performing oral-anal sex with someone who has the virus.
Diagnosis and treatment
Blood tests can detect the hepatitis A virus if someone has it.
There is no cure for the virus, so doctors will often recommend that a person with the infection rests for 1–4 weeks and avoids intimate contact with other people.
Outlook
Although hepatitis A can make people feel very unwell, it rarely causes any complications.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is another virus that causes inflammation of the liver.
Symptoms
In many cases, hepatitis B causes few or no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they can include:
- a rash
- joint pain and stiffness
- fever
- tiredness
- nausea
- loss of appetite
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
- dark urine
- pain or discomfort in the abdomen
Transmission
People with a hepatitis B infection can pass on the virus in their semen or vaginal secretions during oral sex.
Diagnosis and treatment
Doctors can diagnose hepatitis B by performing a blood test. It can take anywhere between 3 weeks and 2 months for the virus to appear in a person’s blood. The test will determine if the infection is acute or chronic.
There is no specific treatment for an acute hepatitis B infection, and most people will fully recover after a short amount of time.
Doctors will treat a chronic hepatitis B infection with medication to slow the progression of the virus and support the immune system. People with an acute infection will typically make a full recovery once the virus has run its course.
Outlook
In severe cases, hepatitis B can lead to chronic infection, scarring of the liver, liver cancer, and even death. A vaccine is available to help protect people from this virus, however.
HIV
HIV is a virus that affects the immune system, making people with it more prone to other illnesses.
Symptoms

Early symptoms of HIV can include fever and fatigue.
A person will need to undergo a test to receive a diagnosis of HIV, as it does not always cause symptoms.
The symptoms that a person experiences depend on the stage of the HIV virus.
Early stage
People may experience symptoms similar to the flu, which can include:
- fever
- aching muscles
- a sore throat
- chills
- fatigue
- swollen lymph glands
- night sweats
Clinical latency stage
People may experience mild symptoms or none at all during this stage.
Transmission
The risk of passing on HIV through oral sex is very low, and the person giving oral sex would need to have an open wound in their mouth in order to catch it.
With the correct treatment, a person with HIV cannot transmit the virus to another person.
Diagnosis and treatment
A healthcare provider can perform a blood or saliva test to determine whether a person has HIV.
Although there is currently no cure for HIV, it is possible to manage the condition effectively with the correct treatment. Treatment for HIV consists of a regimen of antiretroviral drugs called antiretroviral therapy.
Outlook
If people with HIV take medications as prescribed, they can reduce the amount of the virus in their bloodstream to an undetectable level.
They can live a long and healthy life and avoid passing it on to sexual partners.
Prevention
If people are having sexual intercourse or oral sex, they can take the following steps to help prevent STDs:
- use a condom every time they have sex
- use a dental dam every time they have oral sex
- be in a mutually monogamous relationship where both partners have had STD tests
- get regular tests for STDs
If a person does not have access to a dental dam, they can make one at home using a condom. To make a dental dam, follow these steps:
- Cut off the tip of the condom.
- Cut off the elastic ring at the base of the condom.
- Make one cut down the length of the condom.
- Open the condom up into a square.
- Place the dental dam across the vaginal or anal area.
Summary
There are many types of STD that people can transmit or contract as a result of having oral sex.
People can use a condom or a dental dam to help protect themselves and their sexual partners from STDs.
If a person has an STD, it is important that they and their sexual partners receive the correct treatment to prevent any complications arising.
By using appropriate prevention methods and receiving treatment when necessary, people should be able to enjoy oral sex without the risk of STDs.