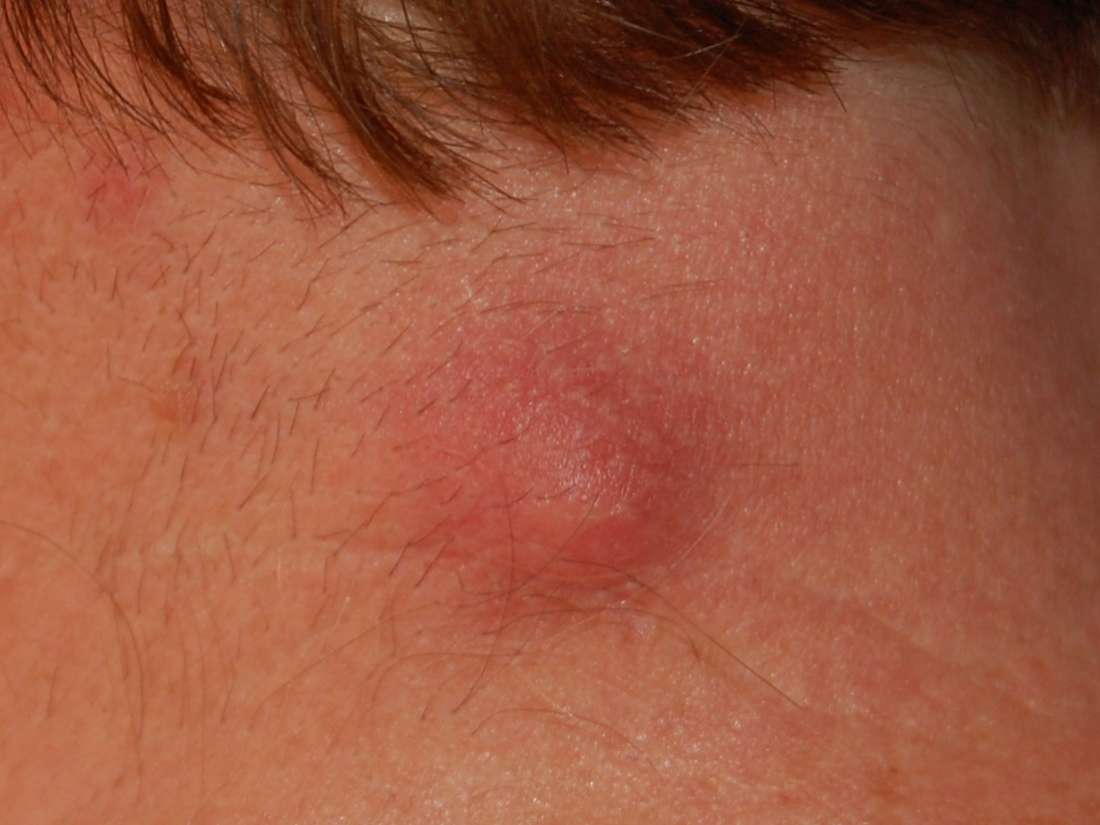
A lump can be alarming, especially if it is not within sight. However, many different conditions can cause a swollen lump on the back of the neck, including benign causes, such as acne and irritation. One cause sometimes leads to another. For example, a boil on the back of the neck can cause the lymph nodes to swell.
The most common causes of a lump on the neck include the following:
Swollen lymph nodes
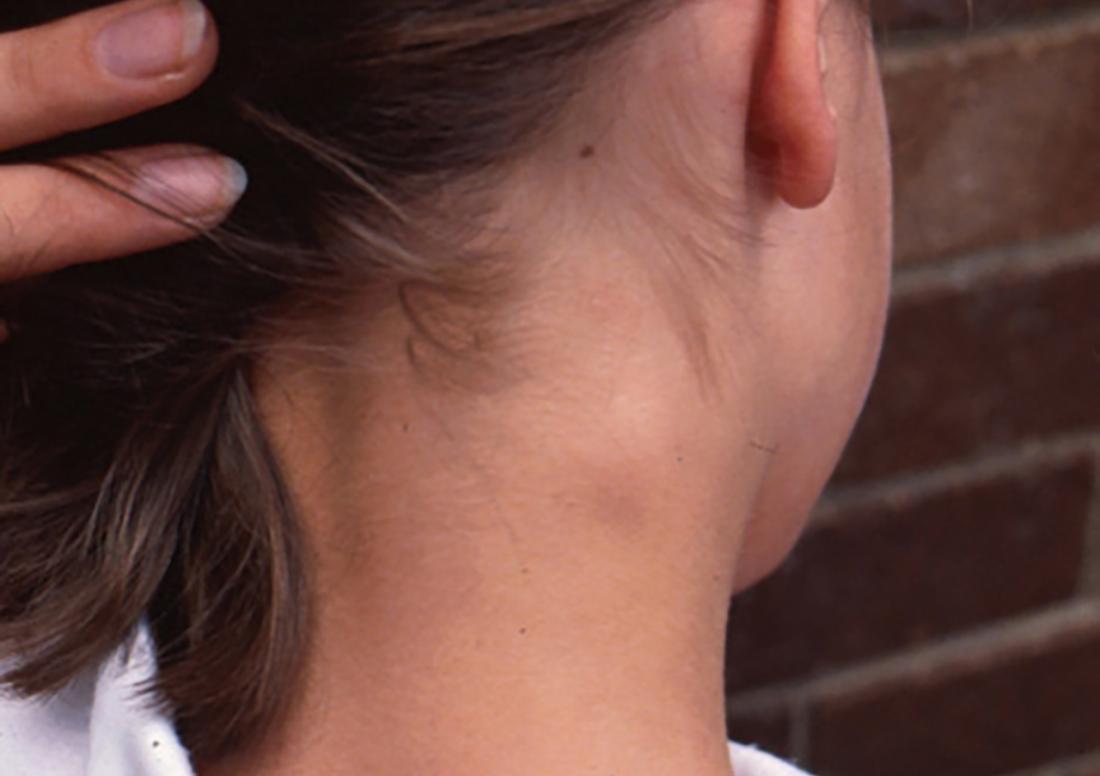

Image credit: Hudson, Bernard, 2010.
The lymph nodes are the body’s drainage system. They help the immune system get rid of bacteria, viruses, and dead cells. Lymph nodes sometimes swell, especially if the body is fighting an infection.
Several lymph nodes run along the back of the neck on either side of the spine. There are also lymph nodes behind each ear. A tender lump that is about the size of a marble and moves slightly when a person touches it may be a swollen lymph node.
Sometimes, lymph nodes swell when there is an infection nearby. Therefore, a swollen lymph node in the neck might be a sign of an ear infection or an infected cyst. Lymph nodes can also swell for no obvious reason. As long as the swelling disappears, there is no reason to worry.
Although it is rare, swollen lymph nodes can sometimes signal a more serious problem, such as cancer. People should see a doctor if the swelling does not disappear after a few weeks.
Acne
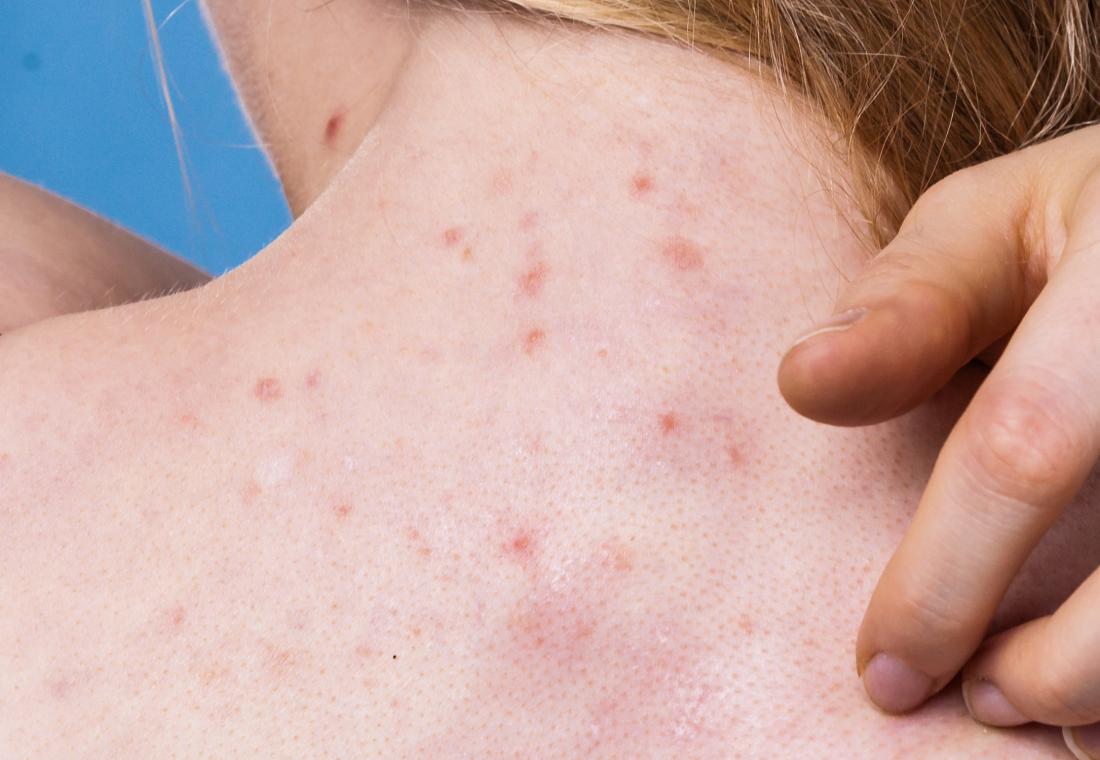
Acne, including blackheads, pimples, and deep cystic acne, can cause lumps and swellings on the back of the neck.
Acne develops when sweat, bacteria, and oil block the pores. Although hormonal changes during adolescence often trigger acne, it can appear at any age.
The neck is a common site for acne. Hair care products, sweat, and clothing can all irritate the back of the neck, making acne worse.
A wide variety of over-the-counter (OTC) remedies may help, as may switching shampoos, keeping the neck clean and dry, and keeping the hair off the neck.
If acne is severe, very painful, or does not respond to home remedies, a dermatologist may prescribe a stronger medication.
Cysts
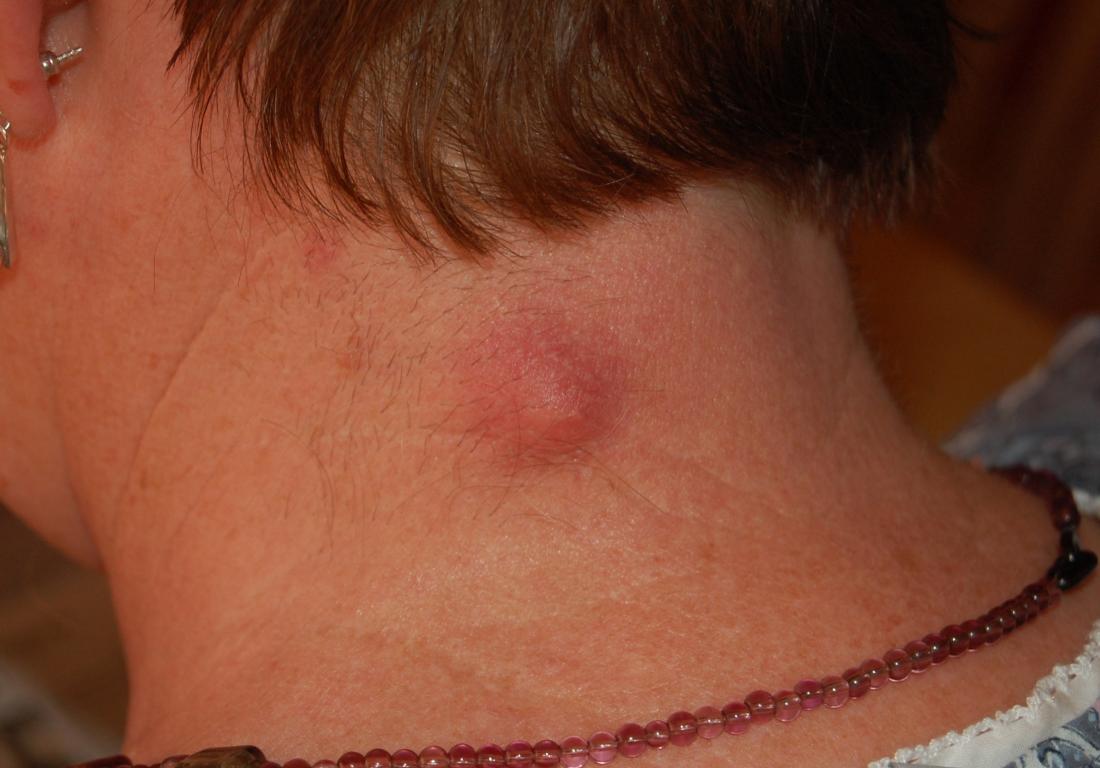
Image credit: Steven Fruitsmaak, 2010.
A sebaceous cyst is a nodule under the skin that contains the protein keratin. These cysts can grow very large. Most are painless, but if they become infected, they may resemble large pimples. Cysts may come and go, or they may continually grow larger.
Some cysts come to a head or ooze when a person squeezes them. However, popping a cyst will not cure it, and doing this can cause an infection. In most cases, a doctor can use a simple procedure to remove a cyst in their office.
If the cyst is painful or red, it is important to see a doctor as this is a sign of infection. Warm compresses and OTC pain medication can also help.
Boils
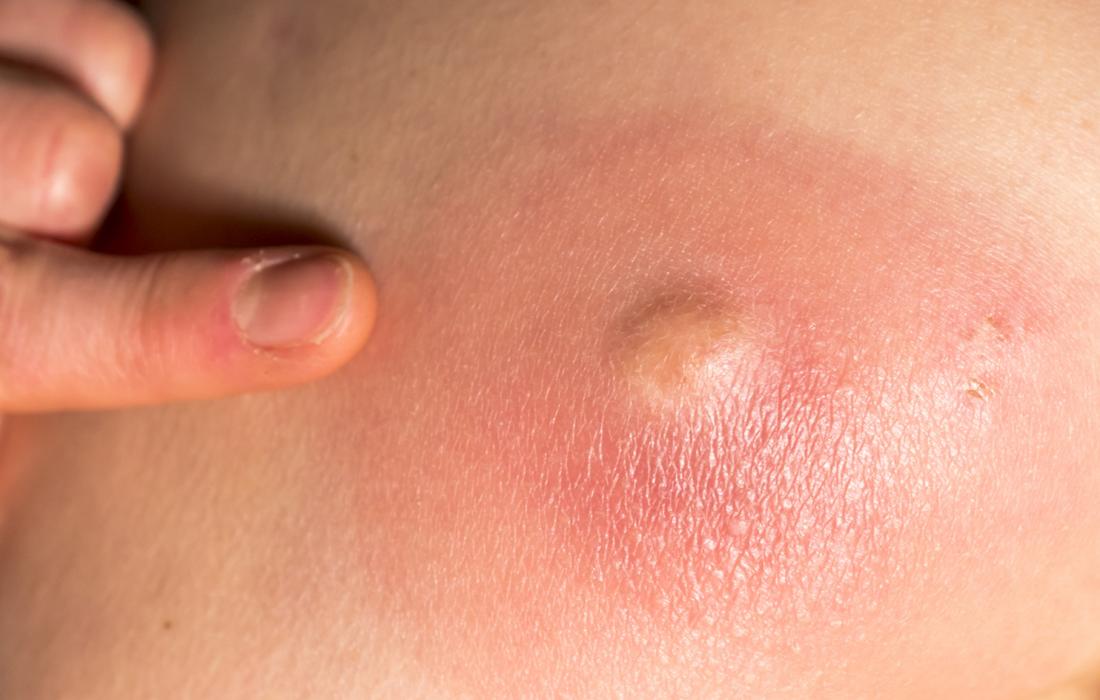
A red and painful bump might be a boil. Boils are local infections, which means that there is an infection in the boil but not the surrounding skin. Cysts, acne, and blocked hair follicles can become infected and turn into boils.
Squeezing a boil can cause the infection to become worse or spread. Instead, people should try applying warm compresses and keeping the area clean.
A person should see a doctor if fever develops or if the boil is very painful or does not go away on its own in a few days. The doctor may drain the boil or prescribe antibiotics.
Moles

In most cases, moles appear during childhood, but new moles can grow at any age. If the lump feels fleshy and is on the skin rather than underneath it or in the muscle, it might be a mole.
Moles themselves are not a problem, but some moles can become cancerous. A person can use a mirror to look at the mole or ask someone else to check it.
Use the ABCDE acronym to check for signs of skin cancer:
- A: asymmetrical mole
- B: uneven or irregular border
- C: uneven color or unusual shades, such as blue and red
- D: diameter greater than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser)
- E: evolving and changing over time
Anyone concerned about their moles should consider scheduling an annual mole check with a dermatologist to ensure that they are all healthy.
Allergic reactions and skin irritation
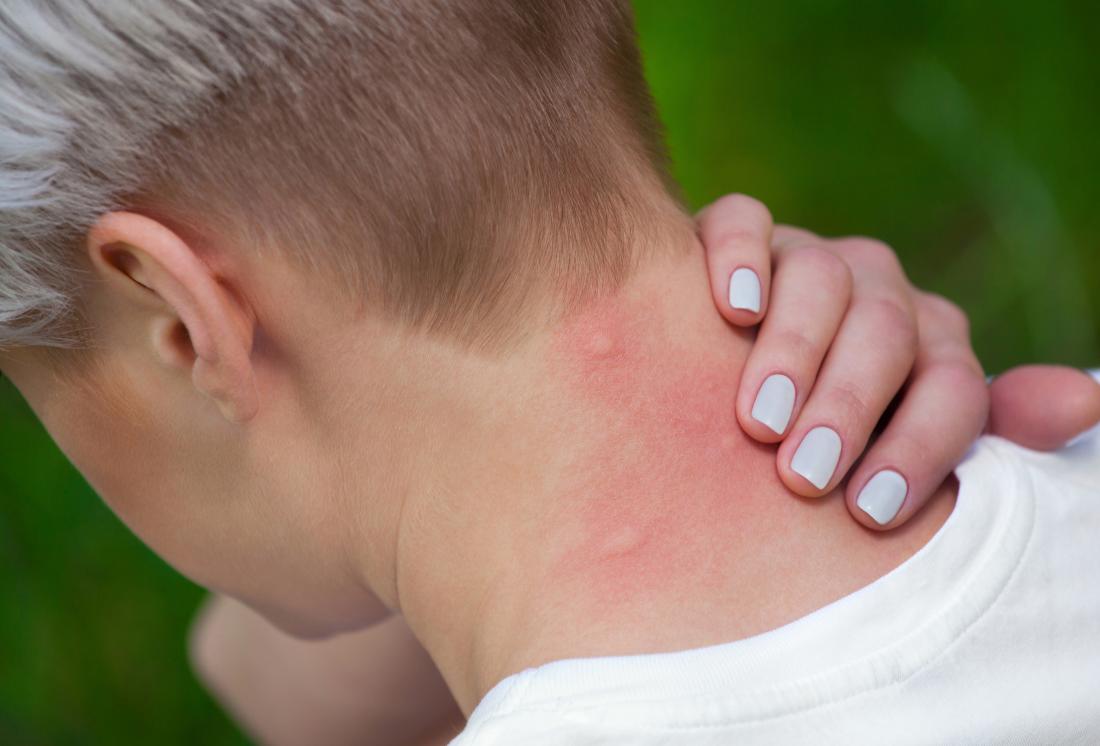

Many substances can irritate the back of the neck.
Shampoo, hair care products, detergent on clothing, and sunscreen may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. Friction from clothing also sometimes irritates the neck and causes a rash.
If the lump is small and itchy or there are dry patches on the neck, this could indicate irritated skin or an allergic reaction.
A person may find that it helps to change detergents, keep the neck clean, keep the hair off the neck, and reduce the number of products that they use on the skin and hair.
If these actions are not effective, a doctor may want to test for allergies and examine the rash to ensure that something else did not cause it.
Muscle knots
Injured or tense muscles can form knots. These tight bands of muscle tissue may be as small as a pea or as large as a baseball. In most cases, they are only palpable underneath the skin and will not cause a visible lump or bump above the skin.
The neck is a common site for muscle pain and tension. Spending consecutive days being hunched over a desk and looking at a computer can irritate the muscles that connect the head to the neck at the hairline. Muscle knots, also called myofascial trigger points, are a sign that the muscles are tense. However, they do not indicate a serious health problem.
A lump is likely to be a muscle knot if:
- it is in a band of muscle rather than above a bone or on the skin
- pushing on it causes muscle pain or tension in either the knot or the surrounding area
Massage can help with muscle knots. Gentle neck stretches, frequent breaks, and good posture can also be beneficial and may prevent muscle knots from forming.
Summary
It is easy for a person to panic if they feel a lump on the back of the neck. However, most lumps are relatively harmless and very few are real emergencies. If the lump does not hurt and there are no other symptoms, it is usually okay to wait a few days to see a doctor. If the bump does not go away, a person should see a doctor.
Even if the cause is something serious, such as an infection or cancer, early treatment significantly increases the likelihood of a positive outcome. People should not allow fear and anxiety to deter them from seeking medical care.