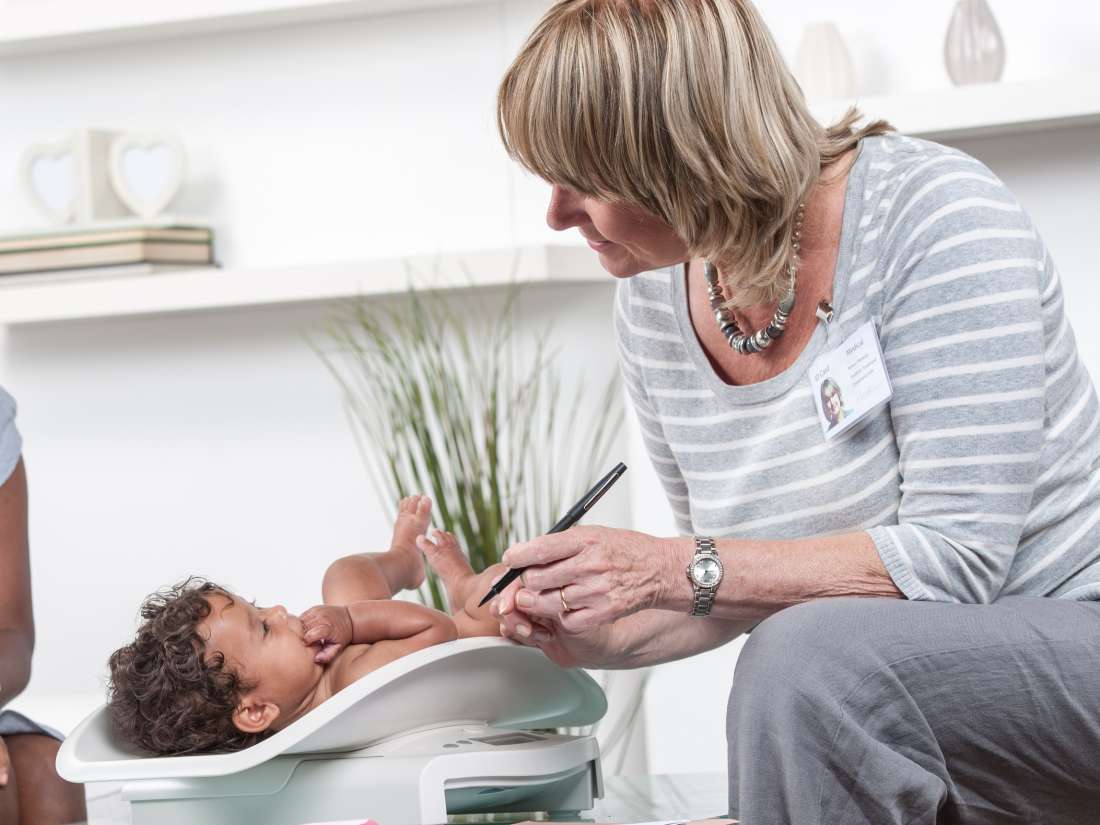
It is important to note that average weight is not the same as “normal” weight. If a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, it does not necessarily mean that anything is wrong with their growth or physical development.
A baby weight chart is one tool that healthcare providers can use to measure a baby’s growth. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend using the World Health Organization (WHO) chart for babies aged 0–2 years.
In this article, learn more about the average baby weight at birth and by month.
Average baby weight

Most full-term babies weigh between 5 lb 8 oz and 8 lb 13 oz.
Like adults, babies can be different sizes. According to the WHO, the average birth weight for male babies born full-term is 7 pounds (lb) 6 ounces (oz). The average birth weight for female babies is 7 lb 2 oz.
Most babies born at 37–40 weeks weigh between 5 lb 8 oz and 8 lb 13 oz. According to March of Dimes, a baby who weighs under 5 lb 8 oz at birth has a low birth weight.
It is common for babies to lose around 10% of their weight shortly after birth. This weight decrease mostly occurs due to fluid loss and is usually nothing to worry about. Most babies gain back the weight within a couple of weeks.
Baby weight chart by age
A baby weight chart plots a baby’s weight on a graph and compares it with the weight of other babies of the same age and sex.
The chart indicates what percentile the baby’s weight falls into. For example, if a baby’s weight is in the 60th percentile, it means that 40% of babies the same age and sex weigh more and 60% weigh less.
The chart below represents baby weights in the 50th percentile. This is the average weight. Male babies tend to weigh a little more than female babies, so the chart is divided by sex.
| Baby age | Female: 50th percentile weight | Male: 50th percentile weight |
| Birth | 7 lb 2 oz (3.2 kg) | 7 lb 6 oz (3.3 kg) |
| 1 month | 9 lb 4 oz (4.2 kg) | 9 lb 14 oz (4.5 kg) |
| 2 months | 11 lb 5 oz (5.1 kg) | 12 lb 4 oz (5.6 kg) |
| 3 months | 12 lb 14 oz (5.8 kg) | 14 lb 1 oz (6.4 kg) |
| 4 months | 14 lb 3 oz (6.4 kg) | 15 lb 7 oz (7.0 kg) |
| 5 months | 15 lb 3 oz (6.9 kg) | 16 lb 9 oz (7.5 kg) |
| 6 months | 16 lb 1 oz (7.3 kg) | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) |
| 7 months | 16 lb 14 oz (7.6 kg) | 18 lb 5 oz (8.3 kg) |
| 8 months | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) | 18 lb 15 oz (8.6 kg) |
| 9 months | 18 lb 2 oz (8.2 kg) | 19 lb 10 oz (8.9 kg) |
| 10 months | 18 lb 11 oz (8.5 kg) | 20 lb 3 oz (9.2 kg) |
| 11 months | 19 lb 4 oz (8.7 kg) | 20 lb 12 oz (9.4 kg) |
| 12 months | 19 lb 12 oz (8.9 kg) | 21 lb 4 oz (9.6 kg) |
What to expect
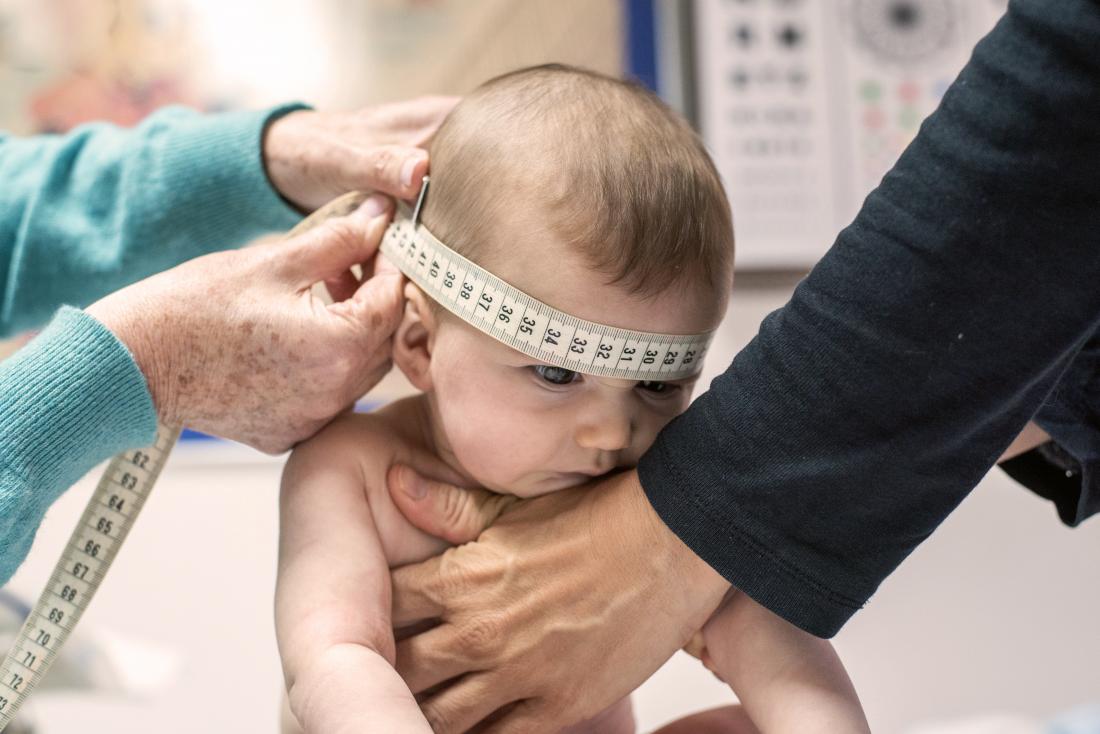
A baby’s length and head circumference are other indicators of their physical development.
Try not to focus too much on weight as the only indicator of physical development. Other measurements that indicate physical development include the baby’s length and their head circumference.
Combining these three measurements gives doctors an indication of how the baby is growing compared with other babies of the same age and sex.
Babies grow and gain weight the fastest within the first 6 months of life. Although it can vary, babies tend to gain around 4–7 oz per week in the first 4–6 months.
Weight gain then slows slightly, with an average gain of around 3–5 oz per week when the baby is aged 6–18 months.
On average, babies triple their birth weight by their first birthday.
Infant growth patterns do not follow a textbook schedule, however. Some babies gain weight steadily and will stay in the same percentile or close to it for several months.
In other cases, a baby’s weight can increase rapidly, which may signal a growth spurt. Growth spurts can occur at any time, and sometimes, a growth spurt will move a baby up to a new weight percentile.
What affects baby weight?
Several factors can affect how fast a baby gains weight. These factors include:
Sex
Although it can vary, male babies are often bigger at birth than female babies, and they typically gain weight a little faster during infancy.
Nutrition
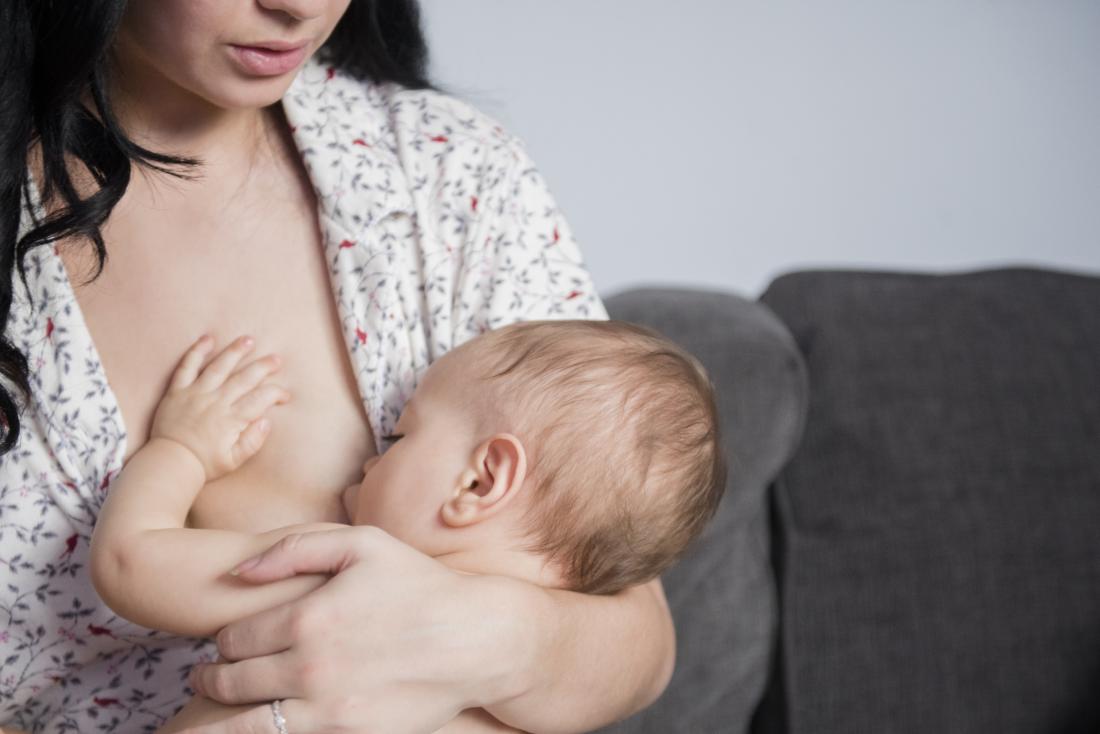

Breastfed babies tend to gain weight and grow faster in the first 6 months.
Weight gain and growth rates can also vary depending on whether the baby consumes breast milk or formula.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, breastfed babies gain weight and grow faster than formula-fed babies during the first 6 months.
However, that rate of weight gain can shift during the second 6 months. Breastfed babies may gain weight and grow less rapidly than formula-fed babies from 6 months to 1 year.
Medical conditions
Underlying medical conditions can cause a baby to gain weight more slowly. For example, babies with congenital heart defects may gain weight at a slower rate than babies without the condition.
Conditions that affect nutrient absorption or digestion, such as celiac disease, may also lead to slow weight gain.
Prematurity
Babies born prematurely may grow and gain weight more slowly during the first year than babies born at full-term.
However, many babies who are born prematurely gain weight rapidly in the first months and can “catch up” in weight by the first year or so.
Summary
The average birth weight for full-term male babies is 7 lb 6 oz. The average birth weight for female babies born full-term is 7 lb 2 oz.
Baby weight charts can help healthcare providers track a baby’s physical development. These charts compare a baby’s weight with that of other babies who are the same age and sex.
Usually, a doctor looks for steady growth rather than a certain percentile to assess a baby’s physical development.
It is important to remember that even if a baby’s weight is in the lower percentiles, they will not necessarily be short adults. The opposite is also true; larger babies do not necessarily become tall adults.
Knowing average baby weights by month can help a person gauge whether a child is growing well, but these measurements are not the only indication of good health. Doctors will also measure their length and the circumference of their head to look at their overall rate of growth.
