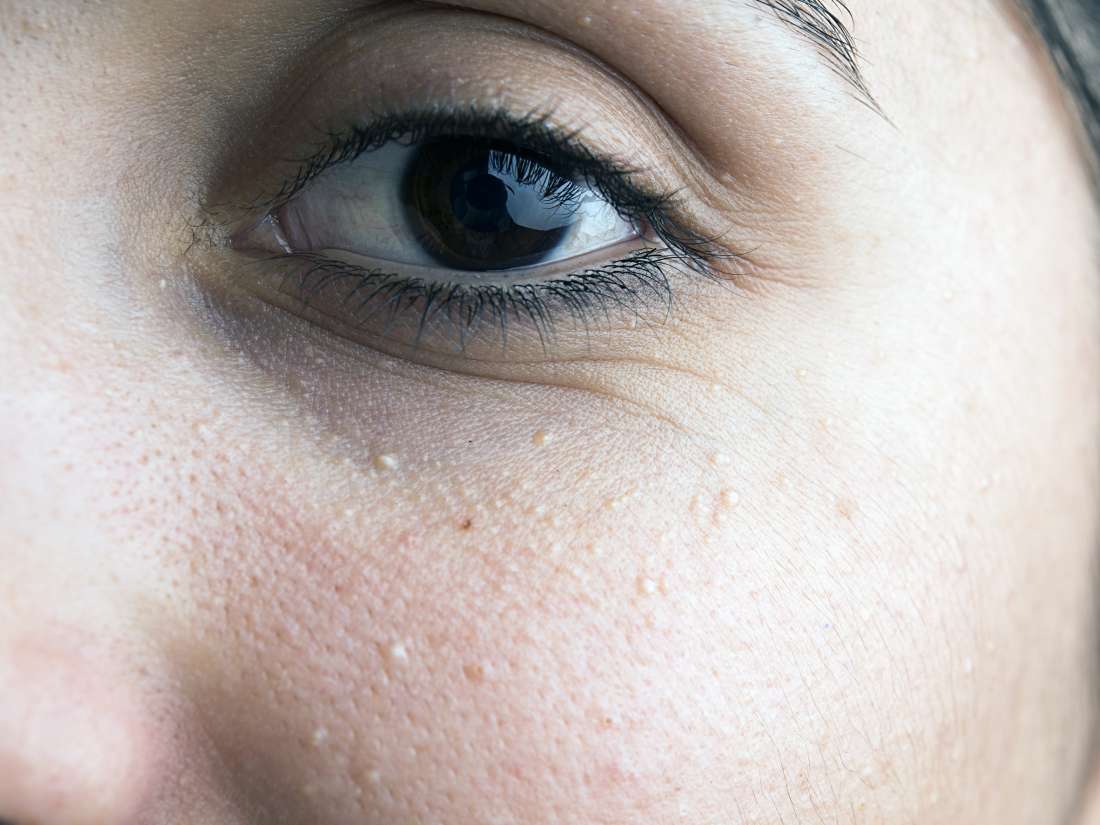
Milia frequently occur in newborn babies, though they also occur in children and adults. It can be easy to mistake milia for acne spots or skin tags.
For some people, including newborns, they may go away on their own, whereas removal may be necessary for others. When milia are close to the eyes, they may need special consideration to avoid damaging a person’s vision.
In this article, learn more about milia under the eyes, including their causes and possible treatments.
What are milia under the eyes?
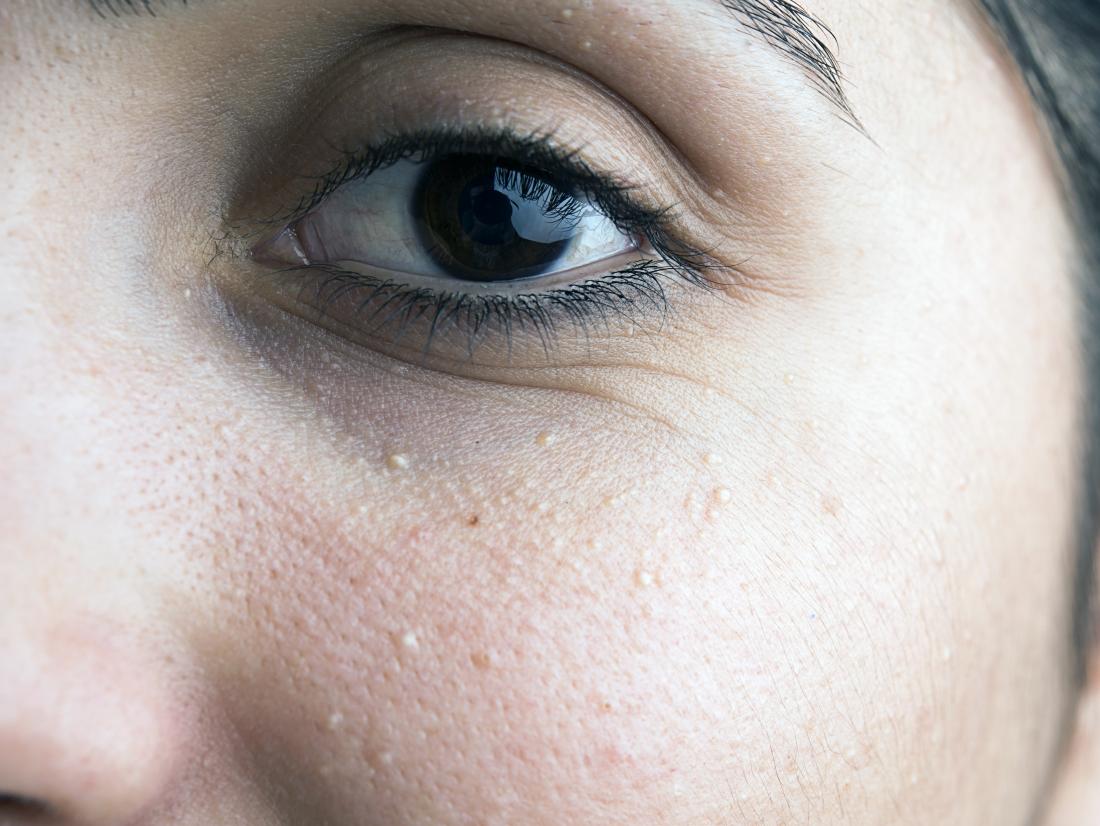

Milia appear as small bumps under the skin.
Milia are small spots, or cysts, that appear under the skin.
Some people may call them “milk spots.”
They are usually white, yellowish, or the same color as a person’s skin.
Milia are not a type of acne, though many people mistake them for acne blemishes or pimples at first. They can appear in other areas on the body, but in adults, they may be more common around the eyes, cheeks, forehead, and genitals.
Milia are actually small collections of trapped keratin. Keratin is what provides the strength to the skin cells, nails, and hair. As these skin cells die off and shed within pores, the keratin may collect and become trapped in the pore, forming a little cyst, or a milium.
When they appear very close to the eyes, a doctor may need the expertise of an ophthalmologist in treating the lesions. However, if they develop a safe distance from the eye, a doctor may feel comfortable performing in-office treatments to remove them.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of milia under the eyes may vary. In some individuals, it may be from trauma or undergoing a cosmetic procedure. However, there is no clear reason why some people develop milia while others do not.
Milia are very common in infants and children. In fact, they affect around 40–50% of newborns. The authors of a 2016 study also note that milia are particularly common among older women.
Some people develop milia after trauma to the skin. In rare cases, a person may develop milia after using a topical medication, such as corticosteroids.
Diagnosis
If a person goes to their regular doctor, they may refer them to a dermatologist, or a skin specialist. A visual examination is usually enough for a dermatologist to be able to diagnose milia.
If a person has a lot of bumps, a doctor may also want to check for underlying conditions that could be leading to multiple milia.
Treatment
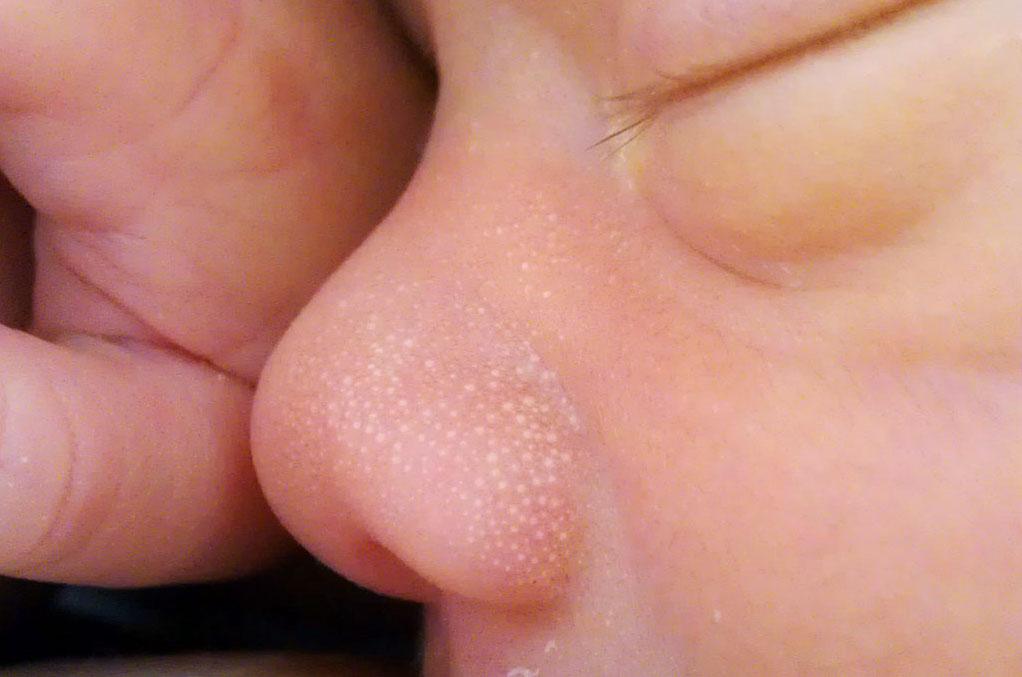
Milia in babies usually clears up over time without treatment.
Image credit: Serephine, 2011
Some cases of milia clear up without any treatment within a few months. Most people who had milia on their face as an infant no longer have any.
However, this is not always the case, and there is no set standard for treatment. Although the bumps are not harmful, many people have cosmetic concerns about milia under the eyes and on the face.
People should never squeeze a milium as they would a pimple. This will irritate the skin and could damage the sensitive skin in the area.
Most at-home milia treatments involve gentle exfoliation or chemical peels. However, it is important to speak to a doctor before using these techniques, especially around the eyes. A doctor may also offer in-office removal.
Chemical peels
Sometimes, a dermatologist may recommend a chemical peel. However, it is important to remember that over-the-counter exfoliative chemicals are unlikely to get rid of milia under the eyes.
Common active ingredients in chemical peels include:
However, the area under the eye is very sensitive, so it is important to take extra care. Always speak to a dermatologist before using any chemical exfoliants.
Professional options
A dermatologist may be able to remove milia under the eyes using techniques in their office. These include:
Extraction
Milium extraction is a common process wherein dermatologists use a tiny needle, or scalpel, to remove part of the skin over the cyst.
Opening the pore in this way allows them to carefully manipulate the keratin out. After this, people will need to take steps toward prevention to keep the milia from coming back.
Laser ablation
During laser ablation, a dermatologist uses a tiny laser to focus on the milium itself, opening the pore.
Cryotherapy
In some cases, cryotherapy may be a worthwhile treatment method. Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy the milia.
However, as the skin below the eye is sensitive, this may not be the best option for milia in this area. It may be painful and cause scarring or pigmentation changes.
Prevention
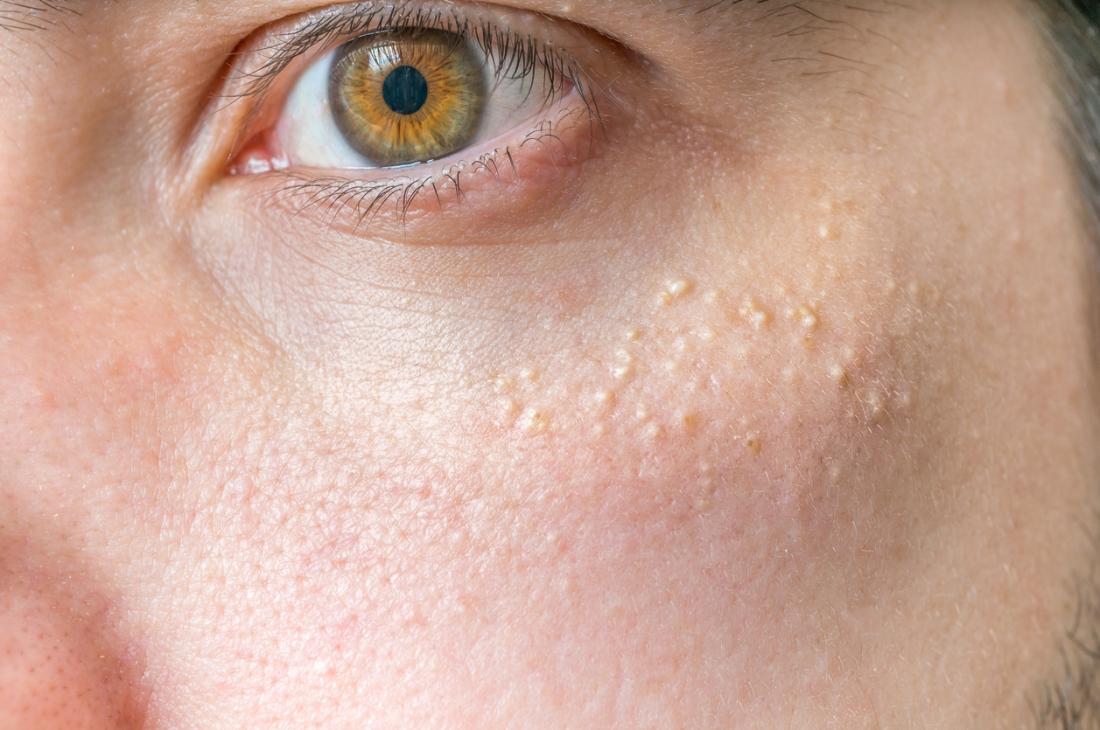
It is not always possible to prevent milia from developing.
Not all cases of milia are preventable, as some people may be more susceptible to them than others.
However, general prevention tips include:
- maintaining a good skin care routine that includes gentle cleansing techniques
- avoiding trauma to the skin
- using a topical or prescription retinoid
Summary
Milia are tiny cysts that develop due to harmless buildups of keratin under the skin. They are common on the face and around and under the eyes.
Milia are not pimples, and attempting to pop them can cause further inflammation and scarring. The pores need to clear out the built up keratin for the milia to go away.
Professional treatments can help remove deeper milia or those in sensitive areas, such as around the eyes.
Anyone who experiences recurring milia in the same area may want to speak to their doctor or dermatologist for a full diagnosis and to discuss treatment options.
